01_StartProject
Code-Dateien
| Dateiname | Aktion |
|---|---|
| CODECode_Urlaub.zip | Download |
PDF-Dokumente
| Dateiname | Aktion |
|---|---|
| PDFFolie_StartProject.pdf | Öffnen |
Videos
| Dateiname | Aktion |
|---|---|
| VIDEOVideo_Urlaub_D | Abspielen |
Lernmaterialien
Startup project
Vaadin
Vaadin ist ein Java-Framework für die Entwicklung von modernen Webanwendungen. Es erlaubt dir, mit Java (oder Kotlin) vollständige UI-Anwendungen zu bauen, ohne dass du dich direkt mit HTML, CSS oder JavaScript beschäftigen musst.
Server-Side UI Framework
- Die gesamte UI-Logik läuft auf dem Server (Java).
- Der Browser zeigt nur die gerenderte Oberfläche an, die Vaadin automatisch per WebSocket/HTTP aktualisiert.
Komponentenbasiert
- Du baust die Oberfläche mit fertigen Komponenten wie TextField, Grid, Button, DatePicker, usw. – ähnlich wie bei Swing/JavaFX, aber fürs Web.
Routing
- Jede View (Seite) ist eine Java-Klasse.
- Über @Route(“zug”) definierst du, unter welcher URL sie erreichbar ist.
Binder & Validation
- Mit Binder kannst du deine Formularfelder direkt an Java-Objekte (DTOs, Entities) binden.
- Unterstützt Bean Validation (@NotNull, @Min, @Pattern …).
Integration
- Funktioniert nahtlos mit Spring Boot.
- Kann auch standalone in einem Servlet-Container laufen (z. B. Tomcat, Jetty).
Modi
- Vaadin Flow: klassisches serverseitiges Java → UI wird automatisch gerendert.
- Vaadin Fusion (heißt jetzt Hilla): Kombination aus Java Backend + TypeScript Frontend.
Create the application
https://start.vaadin.com/app?continue
Mit start playing gelangt man in den design mode
Man muss dann die views definieren. Es können später auch im
IntelliJ views hinzugefügt werden!
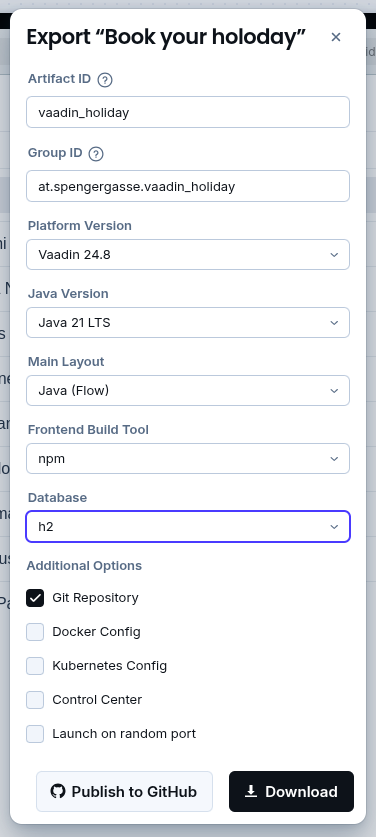
Mit download wird dann das Projekt heruntergeladen.
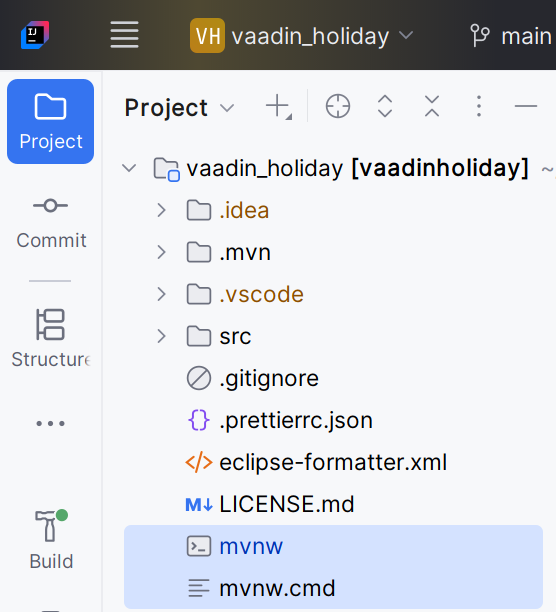
Nach dem Extrahieren wird daraus ein IntelliJ Projekt.

Das Projekt dann öffnen und mit mvwn ausführen.
Es öffnet sich der browser und das Projekt wird ausgeführt.
Layout
Open the project in an IDE. You can download the IntelliJ community
edition if you do not have a suitable IDE already. Once opened in
the IDE, locate the Application class and run the main
method using “Debug”.
For more information on installing in various IDEs, see how to import Vaadin projects to different IDEs.
If you install the Vaadin plugin for IntelliJ, you should instead
launch the Application class using “Debug using
HotswapAgent” to see updates in the Java code immediately reflected in
the browser.
Deploying to Production
The project is a standard Maven project. To create a production build, call
./mvnw clean package -PproductionIf you have Maven globally installed, you can replace
./mvnw with mvn.
This will build a JAR file with all the dependencies and front-end
resources,ready to be run. The file can be found in the
target folder after the build completes. You then launch
the application using
java -jar target/vaadinholiday-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jarProject structure
MainLayout.javainsrc/main/javacontains the navigation setup (i.e., the side/top bar and the main menu). This setup uses App Layout.viewspackage insrc/main/javacontains the server-side Java views of your application.viewsfolder insrc/main/frontendcontains the client-side JavaScript views of your application.themesfolder insrc/main/frontendcontains the custom CSS styles.
Useful links
- Read the documentation at vaadin.com/docs.
- Follow the tutorial at vaadin.com/docs/latest/tutorial/overview.
- Create new projects at start.vaadin.com.
- Search UI components and their usage examples at vaadin.com/docs/latest/components.
- View use case applications that demonstrate Vaadin capabilities at vaadin.com/examples-and-demos.
- Build any UI without custom CSS by discovering Vaadin’s set of CSS utility classes.
- Find a collection of solutions to common use cases at cookbook.vaadin.com.
- Find add-ons at vaadin.com/directory.
- Ask questions on Stack Overflow or join our Forum.
- Report issues, create pull requests in GitHub.